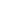
Introduction. L’interféron gamma a un rôle important dans le mécanisme pathologique de l’infection tuberculeuse. Le dosage de l’interféron gamma est très utile dans le diagnostic de la pleurésie tuberculeuse. L’objectif de cette étude était d’évaluer la performance diagnosti- que de l’interféron gamma pour le diagnostic de la cause tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsuda- tives dans les pays où la prévalence de la tuberculose est encore élevée.
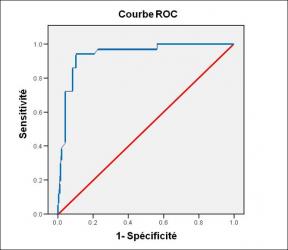
Rationale: Quantitative computed tomography (CT) has been used to phenotype patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). A mixed phenotype is defined as the presence of both airway wall thickening and emphysema on quantitative CT. Little is known about patients with COPD with the mixed phenotype.
ABSTRACT
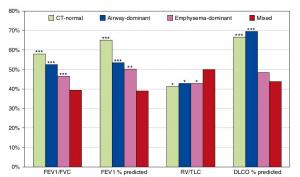
Asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are among the most prevalent lung diseases. In both asthma and COPD, airway inflammation leads to airway remodeling. Parenchyma of the lung is also influenced by disease conditions. Airway wall thickening/ lumen narrowing and parenchymal destruction occur in COPD. In asthma, airway remodeling contributes to the lung parenchyma.
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389