Profusa has announced research findings that suggest the company’s Lumee oxygen platform may help improve the clinical management of patients with critical limb ischemia (CLI) who are undergoing endovascular revascularisation treatment (EVT). The data, from a recent post-market clinical study called OMNIA (Oxygen monitoring near ischaemic areas), were detailed in a series of presentations at the 2020 Leipzig Interventional Course (LINC; 28–31 January, Leipzig, Germany).
The Lumee oxygen platform is a tiny, injectable tissue-integrated biosensor with an intelligent data platform intended for continuous, real-time monitoring of tissue oxygen levels.
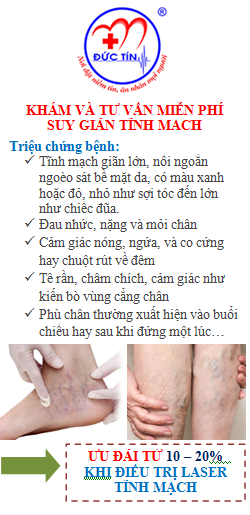
“Performing revascularisation in patients with critical limb ischemia is standard practice, but the tools surgeons and interventionalists typically use to gauge effectiveness of the procedure are not ideal,” said Marianne Brodmann, interim head of the Clinical Division of Angiology, Department of Internal Medicine, at Medical University in Graz, Austria. “These research findings from OMNIA suggest that continuously measuring tissue oxygen may result in better outcomes for these patients.”
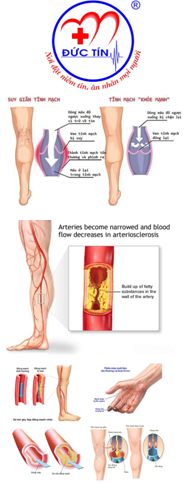
OMNIA, a multicentre trial of the Lumee oxygen platform, monitored tissue oxygen levels in the affected limbs of 35 CLI patients who underwent EVT procedures, which are designed to clear obstructed arteries. Study participants were injected with four Lumee biosensors, three in the foot and one as a reference sensor in the arm. OMNIA collected measurements of oxygen throughout the revascularisation process (with measurements performed before, during, and one, three, six, and twelve months post-procedure). OMNIA also recorded traditional haemodynamic metrics, including ankle-brachial index and toe-brachial index, and clinical assessments of wound healing at each follow-up visit.
The OMNIA data presented by Brodmann showed that increases in tissue oxygen during EVT were significantly higher in patients who experienced wound healing than in those who did not (p<0.01). In addition, tissue oxygen levels during revascularisation were a better predictor of wound healing than traditional clinical measures, such as ankle-brachial index or toe-brachial index (p=0.59 and p=0.14, respectively).
“These findings show the importance of further investigating how continuous tissue oxygen measurements may satisfy an unmet clinical need to objectively evaluate how the increases in blood flow offered by EVT actually translate into nutritive oxygen delivery to the injured tissue,” added Brodmann.
Martin Werner, an angiologist at Hanusch Hospital in Vienna, noted that traditional angiography during EVT does not sufficiently measure microvascular blood flow, a special concern for people with diabetes who may have microvascular impairment. He presented results of a retrospective classification analysis from OMNIA in which continuous oxygen traces measured by the Lumee oxygen platform were analysed throughout EVT. Findings showed that oxygen changes between discrete time points, specifically start and end of EVT, may not be predictive of wound healing, but dynamic changes continually assessed throughout the procedure were.
“These results indicate that continuous measurements of blood flow in the foot during EVT may reveal factors that provide clues to treatment outcome that would have been missed if only measured at the start and end of the procedure,” said Werner.
Stephen Kanick, data science lead for Profusa, presented data from OMNIA that evaluated how Lumee biosensors assess long-term tissue viability following EVT treatments in patients with CLI. Results showed that patients who improved showed larger oxygen increases after EVT and maintained larger oxygen values at a three-month follow-up compared to patients who did not improve.
Miguel Montero-Baker, vascular surgeon and associate professor in the Division of Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, USA, discussed how tissue oxygen measured before, during and after EVT can be combined to provide a more accurate predictor of patient healing. According to Montero-Baker, “The Lumee oxygen platform gives us insights we have not had before about how CLI patients are responding to treatment.”
“These findings from OMNIA affirm the emerging role of injectable biosensors in informing the treatment of patients with limb-threatening ischemia,” said Ben Hwang, chairman and CEO of Profusa. “Being able to monitor biochemical data such as tissue oxygen on a real-time basis may mean the difference between effective interventions and a catastrophic worsening of the condition.”
Source VascularNews
Duc Tin Clinic
Tin tức liên quan
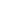
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
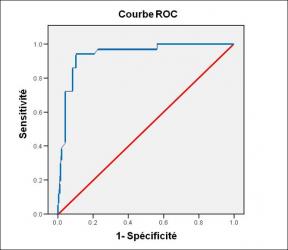
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
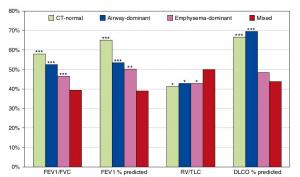
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389