An interim analysis of the Restore EF Study, presented at TCT Connect 2020 (14–18 October, virtual), demonstrates the use of contemporary best practices, including attempting a more complete revascularisation with Impella-supported high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is associated with significant improvement of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), heart failure symptoms, and anginal symptoms at follow-up. The analysis was presented by Mitul Patel, MD, an interventional cardiologist at UC San Diego Health, San Diego, USA.
The ongoing, multicentre, prospective, single-arm study enrolled 193 consecutive qualified patients who underwent a Protected PCI procedure with Impella between September 2019 and September 2020 at 19 hospitals in the USA, representing a variety of hospital settings including rural, urban, community and academic centres. The interim analysis showed:
- Significant median LVEF improvement from baseline to 90-day follow up (31% to 45% p<0.0001). LVEF improvement at 90 days is the study’s primary endpoint.
- Significant reduction of heart failure symptoms with 80% reduction in New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification III/IV at follow up (54% to 11% p<0.001).
- Significant reduction of anginal symptoms with 99% reduction in Canadian Cardiovascular Society (CCS) classification III/IV at follow up (70% to 1% p<0.0001).
“Restore EF demonstrates Impella-supported PCI patients have shown a significant LVEF improvement at 90 days. The study also found a significant improvement in heart failure and anginal symptoms assessed with NYHA and CCS functional classifications,” said Patel. “Taken together, this data validates best practices for treating high-risk PCI patients, including the use of Impella to achieve a complete revascularisation in a single setting.”
“High-risk PCI patients often pose a revascularisation challenge due to patient comorbidities, poor LV function, and adverse haemodynamics, which drive worse outcomes. This research demonstrates the rationale for using Impella support during high-risk PCI to maintain coronary perfusion and support haemodynamics during periods of myocardial ischaemia during long or repeated balloon inflations or atherectomy runs. This allows providers to achieve complete functional revascularisation and the best possible outcomes for our patients,” said Jason Wollmuth, an interventional cardiologist at Providence Health and Vascular Institute, Providence, USA and a co-principal investigator of the Restore EF Study.
Findings from Restore EF will be used to inform the study protocol for the upcoming PROTECT IV Randomised Controlled Trial. PROTECT IV will be a prospective, two-arm trial that will compare complete revascularisation PCI with Impella to complete revascularisation PCI without any planned haemodynamic support. PROTECT IV is part of the Impella clinical evidence pathway to a Class I clinical guideline recommendation for high-risk PCI. The Restore EF study is sponsored by Abiomed.
Source CardiovascularNews
Duc Tin Clinic
Tin tức liên quan
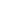
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
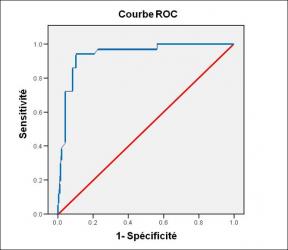
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
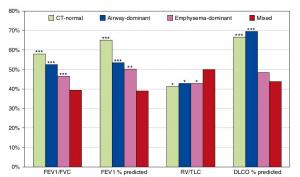
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389