Results of an observational study using optical coherence tomography (OCT) to assess the efficacy of orbital atherectomy in the treatment of calcified coronary lesions using the Diamondback 360 system (Cardiovascular Systems) have been presented at EuroPCR 2021 (18–20 May, virtual).
The study conducted by Surendra Avula (University of Illinois, Chicago, USA) and colleagues and was designed to assess the dual mechanism of action of orbital atherectomy. Twenty consecutive patients with severely calcified lesions identified by coronary angiography were enrolled and treated by a single operator. All patients received a prespecified treatment algorithm including at least three runs of orbital atherectomy at low speed with OCT imaging pre- and post-orbital atherectomy prior to stenting.
There were no angiographic complications in any patients, including 0% dissection, 0% perforation and 0% slow flow/no reflow. Using OCT assessment post-atherectomy, 100% of treated lesions showed calcium fracture (defined as fissures, craters and/or smooth concave ablation) effecting both superficial and deep calcium. Stent delivery and subsequent stent expansion was subsequently achieved in all patients (100%).
Commenting on the results, Avula said: “Orbital atherectomy is used to facilitate stent expansion in severely calcified lesions. In this small observational study we utilised OCT to demonstrate the dual mechanism of action of orbital atherectomy. We clearly observed sanding of intima and fractures of both superficial and deep calcium in the coronary tree. This strategy of peri-procedural OCT imaging in combination with lower speed orbital atherectomy is a paradigm shift in the effective treatment of the calcified coronary tree, and represents a new standard for patient outcomes and safety.”
Severe calcification in coronary lesions impedes optimal stent delivery, expansion and apposition and leads to increased procedural complications and overall inferior results. The Diamondback 360 system uses a dual mechanism of action to treat both superficial and deep calcium, thus restoring native vessel compliance, simplifying procedural workflow, and enhancing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) outcomes, Cardiovascular Systems said in a press release.
Scott Ward, the company’s chairman, president and chief executive officer, said: “This study highlights the benefits of imaging to optimise vessel preparation and reinforces the efficacy of orbital atherectomy’s unique mechanism of action which both ablates and fractures calcium.”
Source CardiovascularNews
Duc Tin Clinic
Tin tức liên quan
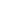
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
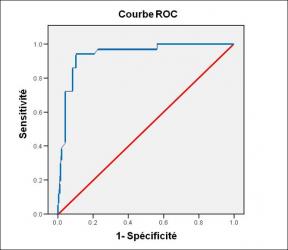
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
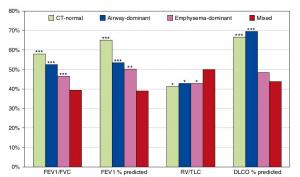
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389