Patients identified by nuclear stress testing as having severe stress-induced myocardial ischaemia are likely to benefit from early coronary revascularisation through either coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), while those with mild or no ischaemia are not, according to a new study published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
For patients with severe ischaemia, early revascularisation was associated with a more than 30% reduction in mortality compared to patients with severe ischaemia who were treated with medication, but no benefit was shown for the other groups, investigator Alan Rozanski (Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, USA) and colleagues reported.
According to the research team, this is the first large-scale study to look at the impact of stress testing on patient management when applied to the full spectrum of patients who have both varying degrees of myocardial ischaemia and heart function. This new study can help guide physicians on how to manage caring for patients with suspected heart disease, the study’s authors suggest.
Physicians order stress tests when they suspect that a patient’s chest pain or other clinical symptoms are from coronary artery disease (CAD), or plaque build-up inside the coronary arteries. These help determine if a patient has obstructive CAD which leads to significant ischaemia. If the ischaemia due to obstructive CAD is severe, physicians can restore adequate blood flow through either CABG or PCI. Nuclear stress testing is the most common stress test used to detect myocardial ischaemia.
“There is keen interest in assessing how measurement of myocardial ischaemia during stress testing can help shape physicians’ decision to refer patients for coronary revascularisation procedures, but this issue has not been well studied among patients who have underlying heart damage,” said Rozanski. “Our study, which evaluated a large number of patients with pre-existing heart damage who underwent cardiac stress testing, finally addresses this clinical void.”
The researchers analysed records of more than 43,000 patients who underwent nuclear stress testing with suspected CAD between 1998 and 2017 at Cedars Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles with a median 11-year follow-up for mortality/survival. The investigators grouped patients according to both their level of myocardial ischaemia during stress testing as well as their left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF).
The study provides two important clinical insights, according to the research team. First, the study showed that the frequency of myocardial ischaemia during stress testing varies according to patients’ heart function. Of the 39,883 patients with normal heart function (LVEF >55%), fewer than 8% of them had ischaemia. However, among the 3,560 patients with reduced heart function (LVEF <45%, which indicates prior heart damage), more than 40% of them had myocardial ischaemia.
The study also showed that the presence of myocardial ischemia increases the risk of death in patients with normal and reduced heart function. Among both groups of patients, performing CABG or PCI procedures was not associated with improved survival among the large percentage of patients who had either no or only mild ischaemia during the cardiac stress test. Among patients with severe ischaemia, coronary procedures were associated with more than 30% higher survival rates compared to those managed with medication only. This was the case for patients with and without heart damage.
“These results confirm the benefits of stress testing for clinical management. What you want from any test when considering coronary revascularisation procedures is that the test will identify a large percentage of patients who are at low clinical risk and do so correctly, while identifying only a small percentage of patients who are at high clinical risk and do so correctly. That is what we found with nuclear stress testing in this study,” adds Rozanski.
“Importantly, the presence of severe ischaemia does not necessarily mean that coronary revascularisation should be applied. New data from a large clinical trial suggests that when medical therapy is optimised it may be as effective as coronary revascularisation in such patients. But regardless, the presence of severe ischaemia indicates high clinical risk which then requires aggressive management to reduce clinical risk.”
Source CardiovascularNews
Duc Tin CLinic
Tin tức liên quan
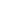
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
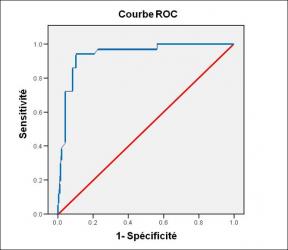
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389