Data presented at an innovation session at the 2022 Structural and Coronary Intervention Course (CSC, 16–18 November, Madrid, Spain) demonstrated an equivalent performance of the Xlimus (Cardionovum) drug-eluting stent (DES) in terms of optical coherence tomography (OCT)-derived endpoints than the Synergy (Boston Scientific) DES, including neointimal volume and neointimal volume weighted by length at six months.
Secondary endpoints, including other OCT parameters, such as in-stent minimum lumen area (MLA) and percentage of strut coverage as well as clinical endpoints, showed no significant differences between the two groups in any of the evaluated parameters within the Xlimit randomised trial.
“The Xlimus sirolimus-eluting stent has the potential to merge the benefits of the ultra-thin strut technology and the bioresorbable polymer in a last-generation DES. The XLIMIT trial showed the reassuring safety and efficacy profile of the Xlimus DES, thus paving the way for future developments of this technology”, said Luca Testa (IRCCS Policlinico S Donato, Milan, Italy) lead principal investigator of the Xlimit trial.
Miquel Craven-Bartle Capella CEO of Cardionovum, commented: “Following our claim ‘Life deserves the best’, we are committed to improving patients’ quality of life by providing innovative solutions and clinical evidence for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. We truly hope that this trial will help generating a larger body of clinical evidence for a better treatment of patients with the coronary artery disease.”
Xlimit is a prospective, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. A total of 177 patients were enrolled from February 2019 and March 2022 in four sites, and randomised in two groups in a 2:1 ratio to Xlimus and Synergy.The primary endpoint, defined as the in-stent neointimal volume evaluated at six-month follow-up with OCT, was evaluated in 118 patients. Instead, 167 patients were included in the population for the secondary endpoints analysis.
Study subjects were mainly males (77.4%) and the mean age was 64 years. Results showed that 47.1% of the population was admitted to the hospital with stable angina/silent ischaemia and 42% for acute coronary syndrome. Diabetic patients represented the 21.5% of the study population.
The neointimal volume was analysed for a total of 137 lesions. Of them, 89 were in the Xlimus group and 48 in the Synergy arm. No significant differences were found (30.7mm3 and 25.5mm3, respectively, p=0.35) between the two groups. The neointimal volume weighted by length showed no significant difference between the Xlimus DES and Synergy DES (1.1mm3 and 0.9mm3 , respectively, p=NS) .The in-stent minimal lumen area at six-month follow-up was 4.3mm2 and 4.7mm2 for Xlimus DES and Synergy, respectively (p=0.25). Strut coverage was above 93% in both groups. Other secondary endpoints, including other OCT parameters as well as clinical endpoints, showed no significant differences between the two groups in any of the evaluated parameters. No safety concern arose from the analyses.
Source CardiovascularNews
Duc Tin clinic
Tin tức liên quan
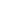
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
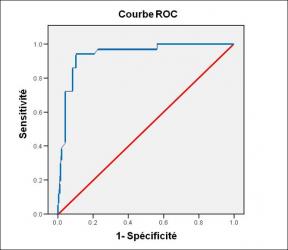
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
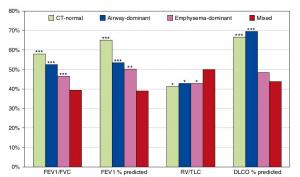
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389