The diagnosis of Pulmonary Hypertension requires a clinical suspicion based on symptoms, physical examination and review of a comprehensive set of investigations.
The diagnosis of Pulmonary Hypertension(PH) requires a clinical suspicion based on symptoms, physical examination and review of a comprehensive set of investigations. This is particularly important for identifying patients who may have more than one cause of PH.
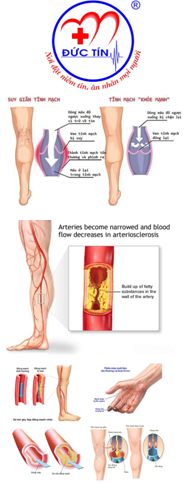
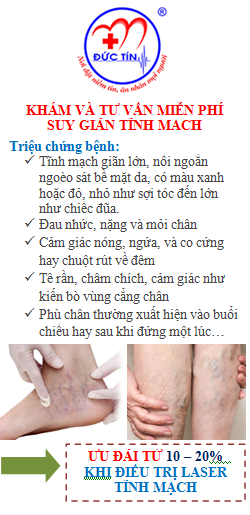
The symptoms of PH are non-specific and mainly related to progressive right ventricular (RV) dysfunction. Initial symptoms are typically induced by exertion that include shortness of breath, fatigue, weakness, angina and syncope.
Less commonly patients may also describe dry cough and exercise-induced nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms at rest occur only in advanced cases. Abdominal distension and ankle oedema will develop with progressing RV failure. In some patients the clinical presentation may be related to mechanical complications of PH including haemoptysis( caused by rupture of hypertrophied bronchial arteries), hoarseness( caused by compression of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve), wheeze ( caused by large airway compression), angina ( caused by compression of the left main coronary artery).
The physical signs of PH include left parasternal lift, an accentuated pulmonary component of the second heart sound, an RV third heart sound, a systolic murmur of tricuspid regurgitation and a diastolic murmur of pulmonary regurgitation. Elevated jugular venous pressure, hepatomegaly, ascites, peripheral oedema and cool extremities characterize patients with advanced disease.
ECG abnormalities may include P pulmonale, right axis deviation, RV hypertrophy, RV strain, right bundle branch block, and QTc prolongation. But a normal ECG does not exclude the diagnosis.
ESC guideline
Duc Tin clinic
Tin tức liên quan
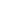
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
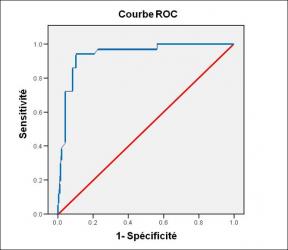
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389