Study Population, End Points, and Cautionary Tales
Considering the appropriate target population for first clinical testing of a novel HF therapy is of utmost importance. In the CUPID trial, patients had to fulfill the criteria of stable,
severely depressed LV contractile function (left ventricular ejection fraction <30%) rendering the patient highly symptomatic (NYHA functional state III or IV), despite stable (>6 months) optimized HF drug treatment including β-blockers, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, and aldosterone receptor antagonists. Importantly, this study only included patients with HF of ischemic origin, although the large animal models used in preclinical testing of SERCA2a did not reflect this population properly. As a precaution because of the proclaimed arrhythmogenic potential of a therapeutic intervention with Ca2+ cycling, all patients included in this study underwent implantation of an implanted cardioverter defibrillator device. Such accommodations may also be a lesson learned from a study using cell therapy with fatal arrhythmia being an effect.
Because the additional value of DNA/RNA-based therapies are tested against optimized HF medication in phase I/II trials, appropriate controls are mandatory. After initial feasibility and dose-escalating studies, future credibility of cardiac gene therapy to treat HF will depend on placebo groups and blinding as essential features. Myocardial biopsy, alike after cardiac transplantation, may be 1 possibility to learn about PD and potential inflammatory adverse effects. As one of the potentially most constraining factors, patients need to be screened for neutralizing antibodies against the administered AAV serotype to exclude the possibility of reduced therapeutic effectiveness.105 Vehicle-related side effects that also need to be thoroughly investigated might include inflammation, viral shedding, and associated insertional mutagenesis. This may pose a major issue for broad application of gene therapy and needs to be addressed by further vector optimization.
To eliminate potential side effects it is worth the effort to use controllable or ON/OFF promoter constructs. Moreover, dissemination of vector distribution and target gene expression within the germline needs to be monitored and might be controlled by ON/OFF constructs.
As always with novel treatments, ethical considerations and responsibility need to provide the balance when weighing the possibility to improve treatment of HF patients against the remaining uncertainty of an innovative and still only partially understood gene therapy approach.
Conclusions and Perspective
Originating from a visionary therapeutic concept, translational research paved the way for first clinical trials that evaluate safety and efficacy of molecular-targeted inotropic therapies with the aim to restore cardiac performance and interrupt the vicious cycle of HF. Although phase I/II trials already indicate safety, phase III results detailing therapeutic efficacy are eagerly awaited. With more therapeutic innovations to come, rigorous evolution in critical areas such as dynamic gene expression control, PK and PD of therapeutics, and holistic understanding of therapeutic modes of action and companion diagnostic development mark the entry to the next generation HF gene therapy, which might eventually become clinical reality.
Source ahajournals.org
DUC TIN Surgical Clinic
Tin tức liên quan
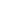
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
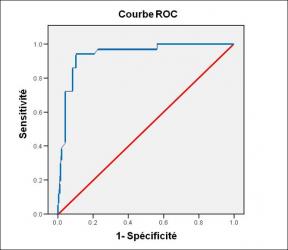
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
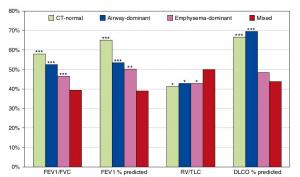
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389