Coronary artery atherosclerosis is the single largest killer of men and women in the United States.
It is the principal cause of coronary artery disease (CAD), in which atherosclerotic changes are present within the walls of the coronary arteries. See the image below.
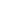
Cardiac catheterization and coronary angiography in the left panel shows severe left anterior descending coronary artery stenosis. This lesion was treated with stent placement in the left anterior descending coronary artery, as observed in the right panel.
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of coronary artery atherosclerosis include the following:
-Chest pain
-Shortness of breath
-Weakness, tiredness, reduced exertional capacity
-Dizziness, palpitations
-Leg swelling
-Weight gain
-Diaphoresis
-Stable angina pectoris
-Intermittent claudication
-Mesenteric angina
-Tachycardia: Common in persons with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
-High or low blood pressure
-S 4 gallop: A common early finding
-S 3 gallop: An indication of reduced left ventricular function
-Heart murmurs
-Tachypnea
-Xanthelasmas
-Livedo reticularis
-Syncope
-Leg edema
-Rales
Diagnosis
Laboratory tests:
-Complete blood count (CBC)
-Chemistry panel
-Lipid profile
-Thyroid function tests: To exclude thyroid disorders
-Blood glucose and hemoglobin A 1C (HbA 1C) measurement: Appropriate in patients with diabetes mellitus
-Myocardial fractional flow reserve (FFR)
-Coronary flow reserve (CFR)
-Lipid studies
-C-reactive protein level
-Serum markers
Imaging studies:
-Echocardiography
-Nuclear imaging
-Computed tomography
-Electron beam CT scanning
-Optical coherence tomography imaging
-Magnetic resonance imaging
-Positron emission tomography
-Coronary angiography
-Doppler velocity probes
-Ultrasonography
Management
The following are used in the management of angina :
-Nitrates
-Beta blockers
-Statins
-Calcium channel blockers
-Ranolazine
Other agents used in the treatment of coronary artery stenosis or to aid in the management of stable coronary artery disease after intervention include the following:
-Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors to reduce blood pressure
-Antiplatelet agents for acute coronary events
-Intravenous glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors
-Aspirin
-Clopidogrel
-Ticlopidine
-HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, or statins to lower LDL cholesterol levels
Treatment procedures for coronary artery atherosclerosis include the following:
-Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
-Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
-Partial ileal bypass
In high- and intermediate-risk patients with 3-vessel disease, PCI was associated with significantly higher rates of revascularization and of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events than CABG ; the 2 procedures were equally effective in the treatment of low-risk patients with 3-vessel disease and in low- and intermediate-risk patients with left main CAD.
Source emedicine.com
Duc Tin Surgical Clinic
Tin tức liên quan
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389