A programme designed to help myocardial infarction patients with the transition from hospital to outpatient care can reduce readmissions and deaths and increase the number of patients keeping follow-up appointments, a new study suggests. The study—from the Sanger Heart and Vascular Heart Care Navigation Team—were presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Cardiovascular Summit (14–16 February, Orlando, USA).
CK-MB isoforms
The CK-MB isoenzyme exists as 2 isoforms: CK-MB1 and CK-MB2. Laboratory determination of CK-MB actually represents the simple sum of the isoforms CK-MB1 and CK-MB2. CK-MB2 is the tissue form and initially is released from the myocardium after MI. It is converted peripherally in serum to the CK-MB1 isoform rapidly after symptom onset.
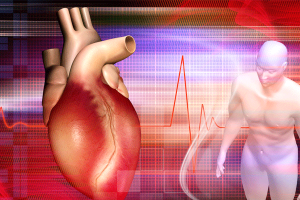
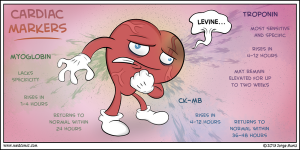
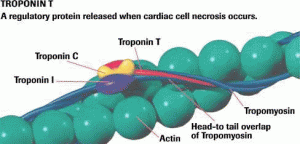
Cardiac markers are used in the diagnosis and risk stratification of patients with chest pain and suspected acute coronary syndrome (ACS). The cardiac troponins, in particular, have become the cardiac markers of choice for patients with ACS.
Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD)ddefined as acute coronary syndromes (ACSs), a history of myocardial infarction (MI), stable or unstable angina, coronary or other arterial revascularization, stroke, transient ischemic attack, or peripheral arterial disease presumed to be of atherosclerotic origindis the leading cause of morbidity and mortality for individuals with diabetes and is the largest contributor to the direct and indirect costs of diabetes.
Background
The incidence of digitalis toxicity has declined in recent years, due to decreased use of this drug along with improved technology for monitoring of drug levels and increased awareness of drug interactions. Nevertheless, cardiac glycoside toxicity continues to be a problem in the United States because of the wide use of digoxin (a preparation of digitalis) and its narrow therapeutic window.
Background
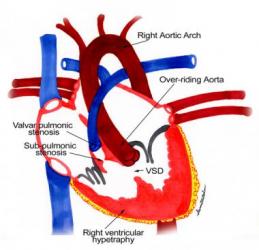
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is one of the most common congenital heart disorders (CHDs). This condition is classified as a cyanotic heart disorder, because tetralogy of Fallot results in an inadequate flow of blood to the lungs for oxygenation (right-to-left shunt) (see the following image). Patients with tetralogy of Fallot initially present with cyanosis shortly after birth, thereby attracting early medical attention.
Background
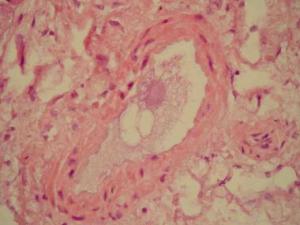
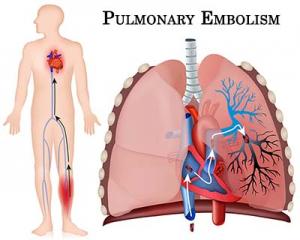
For those who manage major trauma victims, the topic of fat embolism weighs heavily on the mind. The incidence of this problem can approach 90% in patients who have sustained major injuries. If it progresses to the rare clinical entity known as fat embolism syndrome (FES), a systemic inflammatory cascade affecting multiple organ systems, morbidity and mortality are high. Accordingly, swift diagnosis and treatment of fat embolism are paramount for ensuring the survival of this patient population.
Overview
Ventricular repair, or cardiorrhaphy, has long been one of the most dramatic and lifesaving procedures performed in the emergency department. Around 3000 BC, in the Edwin Smith Surgical Papyrus, the first reports of trauma to the thorax were described.
Background
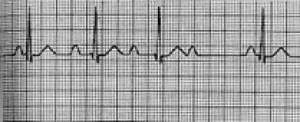
Atrioventricular (AV) block occurs when atrial depolarizations fail to reach the ventricles or when atrial depolarization is conducted with a delay. Three degrees of AV block are recognized.
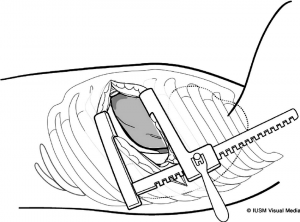
1) PEA by Lateral Thoracotomy
PEA is almost fully established as a method of treatment of CTEPH. Lateral thoracotomy had been used before PEA by median sternotomy with cardiopulmonary bypass and deep hypothermic intermittent circulatory arrest was established as the standard technique. The indications for PEA by lateral thoracotomy are similar to those for the method by median sternotomy, though this procedure is currently considered for only a limited number of patients.
1 Diagnosis
Diagnosis of idiopathic chronic PTE with PH (CTEPH) as a condition requiring treatment should be made according to the criteria for diagnosis provided by the Specific Disease Respiratory Failure Study Group of the MHLW (Table 7). CTEPH should be suspected in patients with exertional dys- pnea. Patients in whom CTEPH is suspected should be iden- tified based on the typical symptoms and clinical findings listed in Table 7.
I. THE GENERAL PRINCIPLE
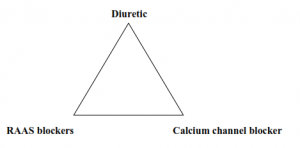
- Treatment is based on the principle of “ pathology triangle of the elderly”.
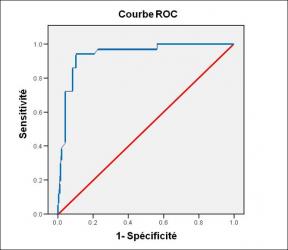
Performance diagnostique de l’interféron gamma dans l’identification de l’origine tuberculeuse des pleurésies exsudatives
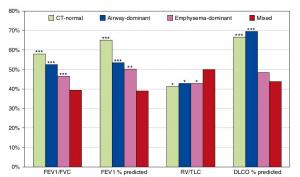
A Mixed Phenotype of Airway Wall Thickening and Emphysema Is Associated with Dyspnea and Hospitalization for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.
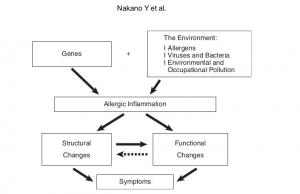
Radiological Approach to Asthma and COPD-The Role of Computed Tomography.

Significant annual cost savings found with UrgoStart in UK and Germany
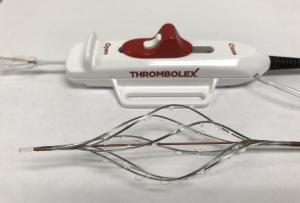
Thrombolex announces 510(k) clearance of Bashir catheter systems for thromboembolic disorders
Phone: (028) 3981 2678
Mobile: 0903 839 878 - 0909 384 389